Creating Data Agents in Microsoft Fabric: A Complete Guide

Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, organizations need tools that allow them to interact with, automate, and analyse data efficiently. Microsoft Fabric, with its unified analytics platform, makes this possible by integrating data engineering, data warehousing, and AI capabilities.
One of its powerful features is Data Agents, which act as automated assistants that can access, analyse, and transform data based on your instructions.
What are Data Agents?
A Data Agent is a specialized AI-powered assistant within Microsoft Fabric that can:
- Access multiple data sources (SQL, Excel, APIs, or external systems).
- Transform and analyse data using automated workflows.
- Respond to queries and provide actionable insights in real-time.
Think of it as your personal data analyst that never sleeps.
Why Use Data Agents?
Before diving into creation, let’s look at why Data Agents are useful:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Tasks like data cleansing, report generation, and trend analysis can be automated.
- Improved Decision-Making: Agents can provide insights quickly, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions.
- Seamless Integration: Data Agents can connect across Microsoft Fabric components—data lakes, warehouses, notebooks, and AI tools.
- Custom Workflows: You can configure Agents to follow unique business logic, ensuring data is processed according to your requirements
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Data Agents
Here’s a practical roadmap to set up your first Data Agent:
- Access Microsoft Fabric
Ensure you have the necessary permissions to create a Data Agent in your Microsoft Fabric workspace.
Open Microsoft Fabric Studio, which is the central hub for all your Fabric activities.
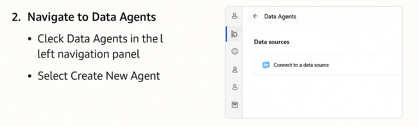
2. Navigate to Data Agents
From the main dashboard:
- Click Data Agents in the left navigation panel.
- Select Create New Agent.
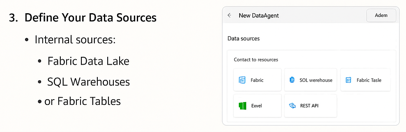
3. Define Your Data Sources
Data Agents need access to your data. You can connect:
- Internal sources: Fabric Data Lake, SQL Warehouses, or Fabric Tables.
- External sources: Excel files, REST APIs, or cloud databases.
Specify connection credentials and access permissions for each data source. Fabric ensures secure connections with enterprise-grade security.
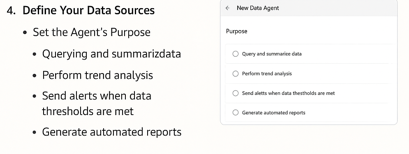
4. Set the Agent’s Purpose
Decide what your Data Agent should do. Some common purposes include:
- Querying and summarizing data
- Performing trend analysis
- Sending alerts when data thresholds are met
Generating automated reports
5. Define Workflows
A Data Agent executes tasks via workflows. Workflows are sequences of steps such as:
- Fetch data from a source
- Clean and transform data
- Apply analytics or AI models
- Output results (report, dashboard, or alert)
Fabric provides a drag-and-drop interface to make workflow creation intuitive. You can also schedule workflows for automatic execution.
6. Add AI or Automation Rules
To make your Agent intelligent:
- Integrate Fabric AI models for predictive analytics or classification.
- Add rules like if-then conditions to automate decisions.
- Configure alerts or notifications to trigger when specific conditions are met.
7. Test Your Agent
Before deploying:
- Run the Agent in a sandbox environment.
- Verify data accuracy and workflow execution.
- Adjust any logic or transformations if needed.
8. Deploy & Monitor
Once satisfied:
- Deploy the Agent to your workspace.
- Monitor its performance using Fabric’s monitoring dashboard.
- Review logs and reports to ensure it’s performing as expected.
Best Practices for Data Agents
- Start Small: Begin with a simple workflow and expand gradually.
- Secure Connections: Use least-privilege access for data sources.
- Document Workflows: Helps team members understand the logic behind each step.
- Leverage AI Models: Use predictive models for tasks like forecasting and anomaly detection.
- Regularly Update Agents: Ensure they adapt to evolving data sources and business rules.
Architecture Diagram
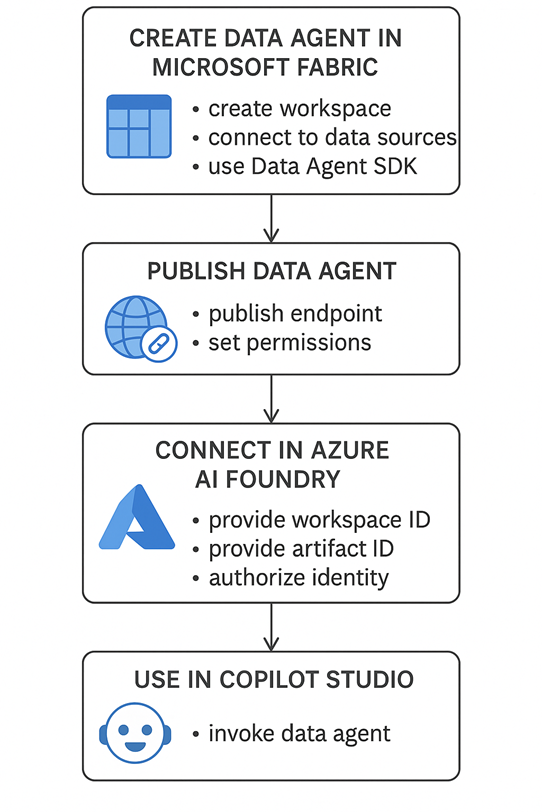
Conclusion
Data Agents in Microsoft Fabric empower organizations to automate workflows, gain real-time insights, and make data-driven decisions with minimal manual effort.
Whether you are a data engineer, analyst, or business user, learning to create and optimize Data Agents can dramatically enhance your productivity and analytical capabilities.
By following the steps outlined in this blog, you can start building intelligent, reliable, and secure Data Agents tailored to your organization’s needs.
Microsoft Fabric is evolving rapidly, and Data Agents are at the forefront of making enterprise data more actionable than ever. If you’re ready to embrace automation and AI in your analytics workflow, now is the perfect time to start experimenting with your first Data Agent.
